Fatty liver disease, which occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver, is increasingly common due to modern lifestyles and diets. While medical advice is essential for managing this condition, making smart dietary choices can significantly improve liver health. Here’s a guide to the best foods for fatty liver that can help reduce fat accumulation and promote liver function.
There are two types of fatty liver disease.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Caused by poor diet, obesity, insulin resistance, and other metabolic issues.
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
NAFLD is more common and can be managed through lifestyle changes, particularly diet.
Now let’s see what the best 10 foods are for fatty liver (1),(2).
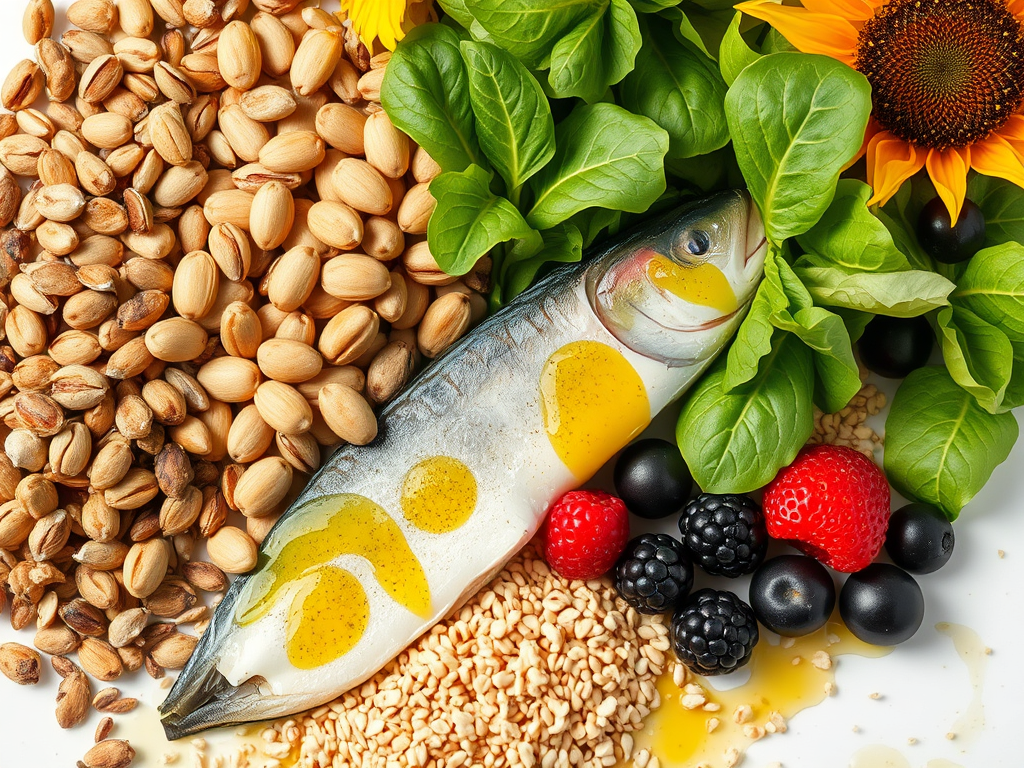
1. Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, and lettuce are rich in antioxidants and nutrients that combat inflammation and reduce fat levels in the liver. Studies suggest that increasing your intake of green vegetables can significantly improve liver health (3).
Tip: Add leafy greens to smoothies, salads, or stir-fries.
2. Fatty Fish
Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which reduce inflammation and help regulate fat metabolism in the liver (4).
Tip: Enjoy grilled or baked fatty fish at least twice a week.
3. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants. These foods can reduce inflammation and improve overall liver function (5).
Tip: Sprinkle nuts and seeds over yogurt, oatmeal, or salads.
4. Whole Grains
Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and other whole grains are rich in fiber and help maintain stable blood sugar levels. This is crucial for preventing further fat buildup in the liver (6).
Tip: Replace refined grains with whole grains in your meals.
5. Olive Oil
Extra virgin olive oil contains healthy monounsaturated fats that support liver health by reducing fat accumulation (7).
Tip: Use olive oil as a salad dressing or for light cooking.
6. Berries
Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are loaded with antioxidants that protect the liver from damage and promote better liver function (8).
Tip: Snack on fresh berries or add them to smoothies and desserts.
7. Green Tea
Rich in antioxidants, green tea helps reduce liver fat and inflammation while promoting detoxification (9).
Tip: Drink 1-2 cups of unsweetened green tea daily.
8. Garlic
Garlic contains compounds that help reduce body fat and improve liver enzyme levels (10).
Tip: Add fresh garlic to your cooking for flavor and health benefits.
9. Turmeric
Turmeric is rich in curcumin, an antioxidant with anti-inflammatory properties that can improve liver function (11).
Tip: Mix turmeric into soups, curries, or teas.
10. Avocado
Packed with healthy fats and fiber, avocados support liver health by reducing oxidative stress and fat accumulation (12).
Tip: Include avocado slices in salads, sandwiches, or smoothies.
Foods to Avoid
While focusing on liver-friendly foods, it’s also important to minimize:
- Refined sugars and carbohydrates (e.g., white bread, pastries)
- Saturated and trans fats (e.g., fried foods, processed snacks)
- Alcohol (especially for alcoholic fatty liver disease)
Lifestyle Tips
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Exercise regularly to help burn excess fat and improve liver function.
- Maintain a healthy weight through balanced eating and active living.
Conclusion
Improving fatty liver disease is possible with consistent dietary and lifestyle changes. Incorporate these liver-friendly foods into your meals to promote better liver health and overall well-being. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice. By making small, sustainable changes today, you can protect your liver for a healthier tomorrow.
Sources
- Chalasani N, et al. “The Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.” American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, 2018.
- Younossi ZM, et al. “Global Epidemiology of NAFLD.” Hepatology, 2019.
- Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA. “The Multiple-Hit Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.” Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 2016.
- Parker HM, et al. “Omega-3 Supplementation and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.” World Journal of Hepatology, 2019.
- Jenkins DJA, et al. “Dietary Fiber and Cardiometabolic Health.” Advances in Nutrition, 2020.
- Schwingshackl L, et al. “Whole Grain Consumption and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2021.
- Santosa S, Jones PJ. “The Role of Olive Oil in Metabolic Syndrome.” Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2020.
- Hosseini A, et al. “Berries and Liver Function.” Nutrients, 2019.
- Akhlaghi M, Bandy B. “Catechins and Their Role in Liver Health.” The Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition, 2017.
- Javad Sharifi-Rad, et al. “Garlic and Its Health Benefits.” International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2020.
- Prasad S, et al. “Turmeric and Curcumin in Liver Protection.” Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2020.
- Mansour-Ghanaei F, et al. “The Effects of Avocado on Liver Health.” World Journal of Gastroenterology, 2019.